What Is an International Bank Account Number (IBAN) and How Does It Work
Navigating the intricate world of international transactions brings up common user queries. One frequent question that Bancoli users have is understanding what an IBAN is and how it relates to SWIFT codes. This article provides clarity to enhance your experience with our platform.
What is an IBAN?
The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is not a payment method but a unique identifier for bank accounts worldwide. It is used in European countries and other nations that have adopted this system. This standardized, internationally recognized code is designed to facilitate international transactions seamlessly and efficiently, making it an essential tool for cross-border payments.
Why is IBAN used?
It is used to simplify and expedite international transactions by reducing the risk of transcription errors. It provides a consistent, clear, and unique identifier for bank accounts, which is crucial for international transactions where different countries have different formats for account numbers.
Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN)
The Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) differs from an IBAN but is an integral part. BBAN represents an individual bank account at a specific financial institution in a particular country. However, it is crucial for domestic and international transactions as it helps accurately identify the recipient’s account.
The Importance of BBAN in International Transactions
The BBAN, or Basic Bank Account Number, is typically used in domestic banking systems in various countries to identify individual bank accounts. While it is crucial for domestic transactions, it is not used in international transactions.
Instead, international transactions rely on the IBAN (International Bank Account Number) and the SWIFT/BIC (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication / Bank Identifier Code) for identification and routing.
Is an IBAN the same as a SWIFT code?
No. While both are used in international banking transactions, they serve different purposes. A SWIFT code identifies a specific bank during an international transaction, whereas an IBAN identifies an individual account involved in the transaction.

The Distinct Roles of IBAN and SWIFT in International Banking
Both codes provide a standardized and secure framework for international transactions. IBAN ensures the accuracy of recipient account numbers, while SWIFT codes identify banks and facilitate secure communication and tracking of transactions. This combination enhances security, efficiency, and accuracy in international financial transactions.
When customers want to make an international transfer, they provide their bank with the recipient’s IBAN and their SWIFT code (BIC). The IBAN identifies the recipient’s account, while the SWIFT code identifies the recipient’s bank.
The customer’s bank initiates a transaction request using the SWIFT network. The request includes all the necessary information, such as the IBAN, SWIFT/BIC codes, and transaction details.
Once verified, the transaction is settled, and funds are transferred from the sender’s account to the recipient’s.
Throughout the process, the sender and recipient banks can track and monitor the transaction’s progress using the SWIFT network. This ensures transparency and accountability.
How do I find my IBAN?
You can find it on your bank statement or by logging into your online banking system. Alternatively, you can request it from your bank. Not all bank accounts have IBANs; typically, only those designated for international transactions do.
Practical Steps to Locate Your IBAN
Finding your IBAN can vary from country and the methods offered by your bank; here are some ways that we recommend on how to find your it:
- Log in to your online banking account.
- Visit your bank’s website.
- Enter your login credentials, such as your username and password.
- Navigate to Your Account Information
- Look for your IBAN on your bank statement. This is usually listed along with your account information, such as the account number, account balance, and transaction history.
- Locate Your IBAN.
- Look for your IBAN in the information section. It should be listed alongside your account number and other account-related information.
- Contact your bank’s customer service.
What does an IBAN look like?
An IBAN consists of up to 34 alphanumeric characters, including a two-character country code, two check digits, and the Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN). The BBAN includes specific bank and account details, and its format varies from country to country.

Decoding the Structure of IBAN
An IBAN consists of a two-letter country code, two check digits, and up to thirty-five alphanumeric characters. These characters include the Bank Identifier Code (BIC), which helps identify bank accounts specifically, and the Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN). The BBAN consists of the branch code and the individual account number.
The IBAN is a standardized format used to identify bank accounts in international transactions; the first two characters represent the country where the bank account is held. These letters are typically the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code for that specific country.
E.g.
United States: US (United States) – Note that the US does not use IBAN for domestic transactions.
Germany: DE (Deutschland)
The following two digits are check digits used to verify the accuracy; these are calculated based on the preceding characters and are essential for error detection. The check digits may vary depending on the country and the bank.
The bank identifier of the IBAN identifies the bank where the account is held. It can vary in length, and the format may differ from country to country. In some cases, it includes the bank’s branch or office identifier.
E.g.
In the United Kingdom, the bank identifier is the sort code (6 digits), followed by an account number (8 digits).
The account number component of the IBAN identifies the individual’s or entity’s bank account. It can vary in length and format and often includes leading zeros to meet the required length.
E.g.
The account number component in Germany can be up to 10 digits long and may contain leading zeros.
Here are a few examples to illustrate the variations in IBAN structure in different countries:
Germany (DE):
IBAN Example: DE89370400440532013000
In this German IBAN, “DE” is the country code, “89” are check digits, “37040044” is the bank identifier, and “0532013000” is the account number.
United Kingdom (GB):
IBAN Example: GB82WEST12345698765432
In this UK IBAN, “GB” is the country code, “82” are check digits, “WEST123456” is the bank identifier, and “98765432” is the account number.
Is the IBAN number the same as the account number?
No, it is not the same as your regular account number. It includes additional information to facilitate international transactions, such as the country code and check digits.
Understanding the Differences Between IBAN and Regular Account Numbers
IBAN and regular domestic account numbers serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Understanding the distinctions between them and the necessity for international transactions is crucial for understanding how IBAN enhances the security and efficiency of cross-border payments.
It reduces the risk of errors, enhances security, and ensures international compatibility, making it an essential tool for the modern global banking system.
Which countries use the IBAN code?
Many countries around the world use this code to facilitate international transactions. However, not all countries have adopted this system. For example, the US and Canada do not use the IBAN for domestic transactions but recognize and process international payments according to the IBAN system.
A Global Overview of IBAN Adoption
The use of this code has been adopted by many countries and regions worldwide, primarily in Europe and other parts of the world. It has brought several benefits to international trade and finance by standardizing and streamlining cross-border payments.
Benefits of IBAN
Standardization
Provide a standardized format for bank account numbers, reducing confusion and errors in international transactions; this makes it easier for financial institutions to process payments accurately.
Efficiency
It streamlines payment processing, making it faster and more efficient. It reduces the time and effort required to validate and process international payments.
Reduced Errors
Including check digits in the IBAN helps detect and prevent errors in account numbers, enhancing the accuracy of cross-border payments.
Improved Security
The IBAN system includes built-in security features, which help protect against fraudulent transactions and unauthorized access to bank accounts.
Global Recognition
While IBAN is internationally recognized, it simplifies trade and finance by ensuring a consistent approach to cross-border payments.
Reduced Costs
Using IBAN can lead to lower transaction costs for international payments, reducing the risk of errors and the need for manual intervention.
SWIFT: The Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication System
SWIFT, or the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, plays an essential role in the international financial landscape. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that transactions are processed swiftly, making international trade and finance more accessible and reliable.
SWIFT Codes: Unique Identifiers for Financial Institutions
SWIFT codes are unique identification codes assigned to each financial institution. These codes are crucial for international money transfers, helping identify the specific bank where the recipient’s account is located.
How to Find and Use SWIFT Codes
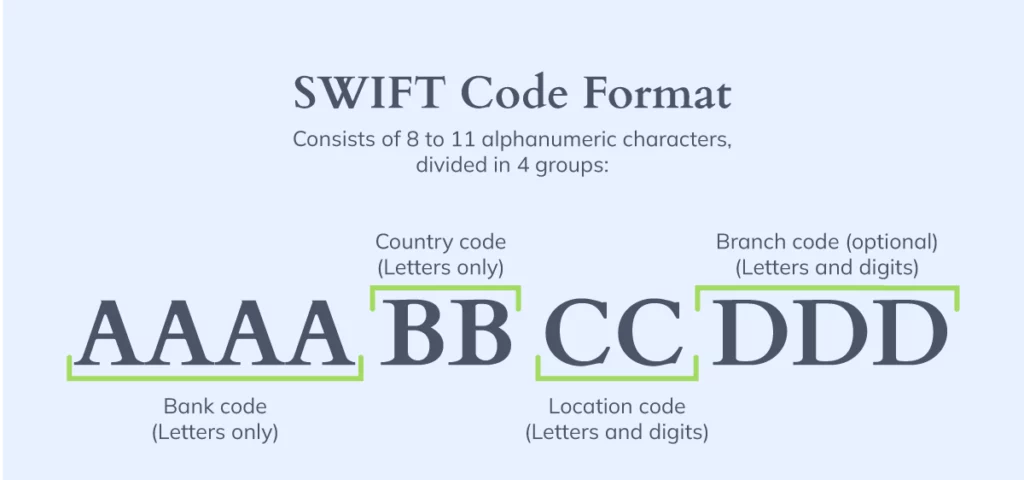
SWIFT codes, or Bank Identifier Codes (BICs), consist of 8 or 11 alphanumeric characters.
These characters are structured as follows:
- The first four letters represent the bank (e.g., ABCD Bank).
- The following two letters represent the country code (e.g., US for the United States).
- The following two characters represent the location code (e.g., NY for New York or LO for London).
- The last three characters, if present, represent the branch code (optional).
There are several ways to locate SWIFT codes; here are some:
- Bank’s website: many banks publish their SWIFT codes on their official websites. Look for a “SWIFT/BIC” section or a page dedicated to international banking.
- Bank statement: your bank statements may include the SWIFT code of your bank.
- Online SWIFT code directories: several online directories list SWIFT codes for banks worldwide. You can use these directories to look up the SWIFT code of a specific bank.
- Contact your bank directly: consider contacting your bank’s customer service. They can provide you with the SWIFT code for your specific branch.
IBAN and SWIFT: Working Together for Efficient Transactions
Both codes are often required when making international transfers. The IBAN provides detailed information about the recipient’s account, while the SWIFT code identifies the specific financial institution.
The Synergy Between IBAN and SWIFT
These codes are two critical components that work in conjunction to facilitate international transactions, providing a seamless and secure experience for users engaged in cross-border trade and finance. These codes identify banks and bank accounts, ensuring the accuracy and security of international money transfers.
IBAN and SWIFT codes work together to ensure that international transactions are routed accurately and securely. IBAN provides a structured and standardized format for identifying bank accounts, while SWIFT codes facilitate the secure exchange of transaction information and direct funds to the correct recipient. This collaboration between codes and networks ensures cross-border trade and finance users a smooth and reliable experience.

In Conclusion
Understanding the roles and functions of IBAN and SWIFT codes is crucial for anyone engaged in international transactions. These codes are designed to make sending and receiving funds across borders as smooth and efficient as possible.




