B2B wire transfers serve as the backbone of business banking, yet many companies underestimate their true costs and complexity. This comprehensive guide takes you from basic concepts to strategic implementation, covering everything businesses need to know about wire transfers in 2025.
Whether you’re a growing business handling your first international payments or an established company optimizing existing processes, this detailed guide provides the knowledge foundation for informed decision-making.
What Is a Wire Transfer?
A wire transfer represents an electronic method of moving funds between entities, serving as a digital alternative to physical cash exchanges. Banks and financial institutions facilitate these transactions, ensuring both security and speed for business operations.
This process involves the sender providing the recipient bank account details to their financial institution. Subsequently, the sending bank communicates with the recipient’s bank through systems like the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network to complete the transfer securely.
Key characteristics of wire transfers include:
- Electronic processing through secure banking networks
- Bank-to-bank communication using established protocols
- Immediate fund availability upon successful completion
- Irreversible transactions once processing begins
- Global accessibility through correspondent banking relationships
B2B wire transfers stand out from other payment methods for their immediate availability of funds and high security standards. However, these advantages come with higher costs and specific processing requirements that businesses must understand for effective implementation.
B2B Wire Transfer Types and Categories
Understanding the various categories of B2B wire transfers enables businesses to select the most suitable options for specific transaction needs. The two primary categories serve different operational requirements and cost structures.
Domestic Wire Transfers
Domestic wire transfers occur within the same country’s banking system and typically settle within the same business day. These transfers avoid currency conversion complexity while utilizing established domestic banking relationships.
Domestic transfer requirements include:
- Recipient identification: Full legal name matching bank account records
- Bank routing number: Nine-digit ABA number for US institutions
- Account details: Specific checking or business account number
- Transfer amount: Exact dollar amount with purpose notation
- Sender verification: Account ownership and available fund confirmation
Processing speed represents the primary advantage of domestic wire transfers. Most transactions complete within 24 hours when initiated before daily cut-off times, making them suitable for urgent business payments requiring same-day availability.
International B2B Wire Transfers
International B2B wire transfers involve transferring funds across borders and require additional information and adherence to regulatory requirements. These transfers typically take longer due to currency conversion and international banking protocols.
Additional international requirements include:
- SWIFT codes: Eight to eleven-character bank identification codes
- IBAN numbers: International Bank Account Numbers for European recipients
- Correspondent bank details: Intermediary institution information when required
- Compliance documentation: Purpose of payment and regulatory forms
- Enhanced verification: Additional identity and business relationship confirmation
International transfers are more complex due to the involvement of multiple banks and cross-border regulatory requirements. Moreover, currency conversion adds both cost and timing uncertainty to the transaction process.

An Alternative: ACH Transfers for USD Accounts
Many global businesses that use USD to send or receive B2B payments find ACH transfers exceptionally convenient due to their low cost and treatment as local US transfers. This potential is available to businesses at a global scale by opening a multi-currency business bank account and leveraging their USD accounts.
B2B Wire Transfer Costs in 2025
Understanding the true cost of B2B wire transfers requires analyzing every fee component, as the base transfer charge is often eclipsed by hidden costs, primarily currency exchange rate markups. For businesses operating globally in 2025, transparency and avoiding these markups are critical to financial efficiency.
Domestic Wire Transfer Pricing
Domestic wire transfer fees vary by financial partner and account relationship, but remain a flat, predictable fee. Businesses typically incur higher costs for in-person or non-automated transfers.
- Major Banks (Outgoing Fee): US$25US-$45. Often includes fee waivers or discounts for premium accounts.
- Credit Unions (Outgoing Fee): US$15-US$25. Generally offer the lowest flat transaction costs.
- Online/Neo-banks (Outgoing Fee): US$15-US$30. Highly automated transfers usually sit at the lower end.
- Processing Method Surcharge: Initiating a transfer via phone or at a physical branch can add US$5-US$15 to the base outgoing fee.
International Wire Transfer Expenses
- Outgoing Transfer Fees (charged by the sending institution): US$35-US$85.
- Incoming Charges (charged by the recipient’s bank): US$0-US$25.
- Intermediary Fees (deducted from the transfer amount – SWIFT network cost): US$10-US$100 per correspondent bank.
- Compliance Charges (for regulatory screening): US$10-US$25.
- Amendment Fees (for error correction): US$15-US$40.
The Biggest Hidden Cost: Exchange Rate Markups
While flat fees are transparent, hidden currency conversion costs represent the largest capital erosion in international business wire transfers.
Traditional banks routinely apply a significant markup to the interbank exchange rate, the rate they receive, before offering it to the customer.
- Traditional Bank Markup Range: 1% to 7% above the true mid-market rate.
- Major Currency Pairs (e.g., USD/EUR, USD/GBP): Markups typically range from 1% to 3%.
- Emerging Market Currencies: Due to lower liquidity, markups can reach 3% to 7%.
Bancoli Advantage: Zero FX Fees on Global Payouts
Bancoli offers a crucial benefit for businesses with international payroll or supplier payments: Zero FX Fees in payouts from the USD business account to 30+ currencies globally.
This means that, for cross-currency conversions, the exchange rate margin is eliminated, offering businesses unparalleled transparency and maximizing the amount received.

Real Cost Example: Hidden Fees vs. Flat Fees
This comparison shows the difference in total cost for a US$100,000 USD-to-EUR transfer between a traditional bank and a Zero FX Fee platform.
1. Traditional Bank Cost Breakdown (Assuming 3% Exchange Rate Markup):
- Base Wire Fee: US$45 (0.045% of the transfer).
- Currency Markup (3% FX Loss): US$3,000 (The single largest cost).
- Intermediary Fees: US$50 (Unpredictable SWIFT cost).
- Receiving Bank Fee: US$25 (Charged to the recipient).
- Total Transfer Cost: US$3,120 (Representing 3.12% of the transfer amount).
2. Zero FX Fee Platform Cost Breakdown (e.g., Bancoli):
- Base Wire Fee: US$45 (Using the original fee for direct comparison).
- Currency Markup (FX Loss): US$0 (Mid-market rate or Zero FX Fee applied).
- Intermediary Fees: US$50 (Assuming standard SWIFT costs still apply).
- Receiving Bank Fee: US$25 (Charged to the recipient).
- Total Transfer Cost: US$120 (Representing 0.12% of the transfer amount).
Conclusion: By eliminating the currency markup alone, the Zero FX Fee platform reduces total transaction costs by US$3,000, demonstrating that the FX rate is the primary driver of international payment expenses. Businesses must prioritize platforms that offer the mid-market rate, or, ideally, Zero FX Fees for cross-currency payouts.
How B2B Wire Transfers Actually Work
The wire transfer process involves multiple stages and participants working through established protocols. Understanding each step helps businesses prepare appropriate documentation while anticipating potential delays.
Domestic Transfer Process Flow
Domestic wire transfers follow streamlined procedures within established national banking networks. The process begins when businesses contact their bank with complete recipient information and transfer instructions.
The initial verification stage involves confirming account ownership, verifying available funds, and validating recipient information against bank databases. Staff review transfer details for accuracy before processing authorization, as errors can cause delays or misdirection.
Subsequently, network processing occurs through the Federal Reserve’s Fedwire system for US transactions. Wire transfers are processed individually in real-time, rather than in batches, which distinguishes them from ACH transactions that banks handle in scheduled groups.
Finally, settlement and confirmation complete the process within hours during business days. Both parties receive transaction confirmations with reference numbers for accounting records and audit trail maintenance.
International Transfer Complexity
International wire transfers require additional documentation and processing steps due to cross-border regulatory requirements and the involvement of correspondent banking.
Documentation gathering becomes more extensive for international transactions. Businesses must provide SWIFT codes identifying recipient banks internationally, IBANs for European transactions, and detailed correspondent bank information when direct institutional relationships don’t exist.
Moreover, compliance verification increases processing time substantially. Banks conduct enhanced due diligence screening against sanctions lists while requiring purpose of payment documentation for regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
Multi-bank routing characterizes international wire transfers. Funds often pass through correspondent banks that maintain relationships between sending and receiving institutions. Each intermediary processes, verifies, and forwards transactions while applying fees and conversion rates.
Therefore, processing timelines extend from same-day domestic completion to 1-5 business days for international transfers, depending on routing complexity and compliance requirements.
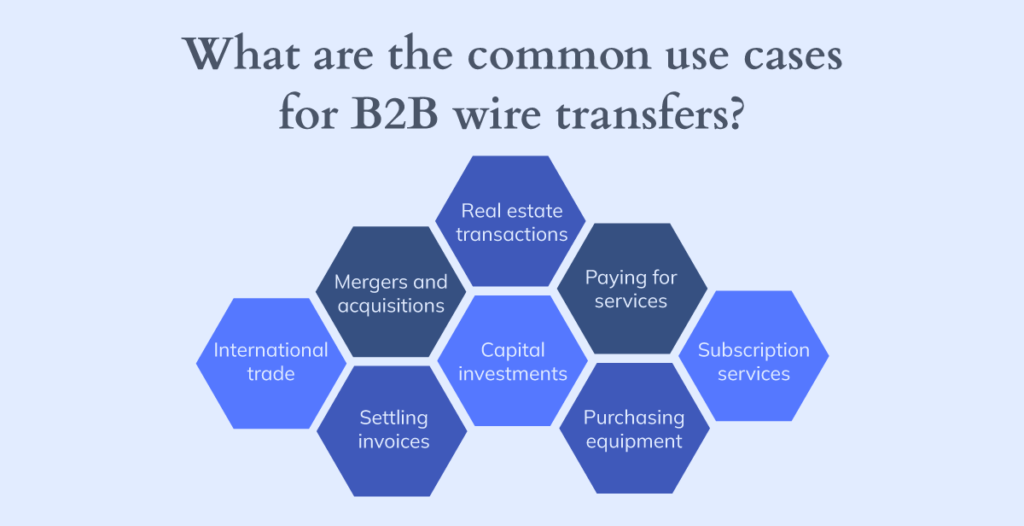
When Businesses Should Use Wire Transfers
Despite costs and complexity, B2B wire transfers remain optimal for specific scenarios where their unique characteristics provide operational value. Understanding when to choose wire transfers versus alternatives helps optimize payment method selection.

High-Value International Business Transactions
International B2B wire transfers become cost-effective for large cross-border transactions, where fees represent a negligible percentage of the total amount. These transfers provide reliable cross-border settlement within 1-5 business days.
Optimal international transaction scenarios:
- Real estate purchases: Legal requirements often mandate international wire confirmation.
- Equipment acquisitions: Large machinery purchases from overseas suppliers requiring secure payment.
- Merger activities: Corporate transactions needing reliable international fund transfer (1-5 days).
- Non-urgent international payments: Supplier payments where 1-5 day processing is acceptable.
- International contracts: High-value agreements requiring secure cross-border settlement.
Cost justification arises when international transaction sizes reach levels at which wire fees are minimal relative to the transaction value. A US$500,000 equipment purchase from overseas with a US$50 wire fee represents a 0.01% cost, negligible compared to the potential operational delays that could result from slower payment methods.
For urgent international payments that require same-day settlement, businesses should consider stablecoin or in-network transfers for large amounts, which enable 24/7 processing without banking delays.
For domestic high-value transactions, businesses can consider ACH or in-network transfers, which offer sufficient security at lower cost than domestic wire transfers.
Time-Critical International Operations
Certain international business operations require immediate payment confirmation and fund availability across borders.
For maximum speed, businesses may also consider adding stablecoin and in-network transfers to their payment stack, enabling 24/7 settlement without the restrictions of banking hours.

Time-sensitive international use cases:
- Supply chain emergencies: Critical material purchases from international suppliers preventing production delays.
- International regulatory deadlines: Cross-border tax payments or compliance fees with specific timing requirements.
- Contract settlements: International legal agreements requiring immediate fund transfer confirmation.
- International logistics: Customs payments or documentation fees enabling international shipment release.
Major B2B Wire Transfer Challenges
While wire transfers offer security and reliability, they present several operational challenges that particularly impact growing businesses, which must manage increasing transaction volumes and international expansion.
High Transaction Costs Impact
High transaction fees represent the most significant B2B payment pain point for companies managing regular wire transfer requirements. These costs accumulate rapidly and affect business profitability regardless of company size.
Fee burden by business size:
- Small businesses: US$500 monthly transfers = US$1,800 annual wire fees.
- Mid-market companies: US$50,000 monthly transfers = US$18,000+ annual fees.
- Growing enterprises: Volume increases compound fee burden faster than revenue growth.
- International focus: Cross-border businesses face 2-3x higher fee structures.
Operational impact extends beyond direct costs. Fee unpredictability complicates international contract negotiations, while administrative overhead diverts finance team resources from strategic activities. Additionally, high payment costs reduce pricing flexibility in competitive markets.
Furthermore, budget forecasting becomes difficult when wire transfer costs vary based on currency pairs, intermediary bank involvement, and processing timing. This unpredictability particularly affects businesses expanding into new international markets.
Processing Delays and Cash Flow Disruption
Payment delays disrupt business operations and strain supplier relationships, creating a cascading effect that can impact the entire business. Manual processing requirements create bottlenecks that limit operational efficiency.
Cash flow timing issues include:
- Working capital delays: 3-5 day processing ties up operational funds.
- Weekend gaps: Banking holidays extend processing unpredictably.
- Emergency scenarios: Same-day processing requires expensive premium fees.
- International complexity: Time zone differences affect completion timing.
Business relationship strain occurs when payment delays affect supplier terms or project milestones. Late vendor payments can jeopardize favorable pricing agreements, while delayed client payments may impact project delivery schedules and customer satisfaction.
Manual processes lead to frequent payment delays, which compound operational challenges as businesses expand their international activities and supplier relationships.

Currency Exchange Complications
International B2B wire transfers face significant uncertainty from currency conversion timing and rate application. Currency conversion complications create financial uncertainty for international businesses.
Exchange rate variables include:
- Market volatility: Rate changes during multi-day processing periods.
- Timing uncertainty: Weekend rate holds, potentially creating unfavorable conversions.
- Markup disclosure: Final conversion costs unknown until transaction completion.
- Multiple conversions: Correspondent banking chains may apply rates at different stages.
The impact of financial planning becomes substantial when currency markups reach 1-7% above market rates. Therefore, businesses struggle to accurately budget international payments when conversion costs remain unpredictable until transaction completion.

To counter this, a key strategic option for businesses making regular cross-border payouts is to leverage platforms offering Zero FX Fees. This modern approach, exemplified by solutions like Bancoli, eliminates the exchange rate margin for payouts from a USD business account to over 30 global currencies, neutralizing the largest hidden cost and making international wire transfers a predictable, flat-fee expense.
Strategic Considerations for Business Wire Transfer Use
Successful wire transfer decisions require practical evaluation frameworks rather than theoretical analysis. Smart businesses use specific questions and criteria to determine when wire transfers provide optimal value versus alternative payment methods.
Decision-Making Questions for Wire Transfer Use
Before initiating any wire transfer, businesses should systematically evaluate whether this payment method aligns with transaction characteristics and operational requirements.
Ask these key questions first:
- Is this transaction over US$100,000, where wire fees are negligible as a percentage?
- Does this international payment need to settle within 1-5 business days specifically?
- Are there legal or compliance requirements mandating wire transfer confirmation?
- Do alternative payment methods effectively cover the required geographic corridor?
- What’s the total cost, including currency conversion (considering options with Zero FX Fees), compared to other alternatives?
- Does the recipient specifically require a wire transfer for their operational processes?
These questions help businesses avoid unnecessary wire transfer costs while ensuring they select an appropriate method for scenarios that require wire transfers.

Additional Evaluation Areas
Beyond the core decision questions, consider these operational factors when evaluating payment methods:
- Financial impact analysis: Fee percentage versus transaction urgency requirements.
- Geographic accessibility: Destination country payment infrastructure capabilities.
- Compliance requirements: Legal mandates versus operational preferences.
- Counterparty expectations: Supplier or client payment method preferences.
- Technology infrastructure: Internal capabilities for implementing alternative methods.
Building Efficient B2B Wire Transfer Workflows
Businesses can optimize wire transfer efficiency by developing systematic workflows and integrating technology. Standardized processes reduce error rates while improving processing speed and administrative efficiency.
Process optimization strategies:
- Template development: Standardized forms for repeat transactions.
- Approval workflows: Systematic authorization procedures for different amounts.
- Documentation systems: Organized storage for required transfer information.
- Status tracking: Systematic monitoring procedures for transaction completion.
- Error prevention: Verification checklists, reducing correction requirements.
Multi-Currency Payment Strategy Development
International businesses benefit from strategic approaches to currency management that reduce conversion frequency and optimize exchange rate timing. However, traditional banking requires separate accounts across multiple institutions, creating operational complexity.
Currency strategy considerations include maintaining balances in major trading currencies, timing conversions for favorable market conditions, and utilizing natural hedging through operational cash flows in multiple currencies.

Global businesses increasingly use unified platforms instead of juggling multiple banking relationships. The most advanced platforms offer local-style accounts (such as dedicated USD and EUR accounts) alongside strategic cost-saving features. For instance, Bancoli’s Global Business Account provides this unified structure, further enhanced by Zero FX Fees for payouts to over 30 currencies, consolidating operational benefits and cost optimization into a single solution.
Multi-Rail Payment Platform Benefits
Businesses are adopting unified payment platforms that consolidate multiple payment methods into a single solution, reducing complexity while expanding payment acceptance capabilities.
Platform advantages include:
- Single integration: Supporting cards, ACH, wires, and stablecoins.
- Simplified reconciliation: Eliminating manual transaction matching.
- Enhanced visibility: Comprehensive transaction visibility across methods.
- Reduced overhead: Simplified vendor relationship management.

Bancoli’s Global Payment Gateway addresses these requirements in a single solution that eliminates the need for multiple banking relationships while expanding customer payment options.
When Alternatives Work Better than B2B Wire Transfers
Payment method selection requires matching solution capabilities to specific transaction characteristics and business operational requirements. Different scenarios favor different approaches for optimal cost and efficiency outcomes.
Alternative method advantages:
- ACH networks: US$0-US$3 costs for domestic transfers under US$25,000.
- Cryptocurrency solutions: 24/7 settlement without banking hour restrictions.
- In-network transfers: Instant transfers in business banking platforms like Bancoli.
Businesses often benefit from diversified payment strategies that leverage optimal methods for different types of transactions, rather than relying on a single payment approach.
Conclusion
Understanding B2B wire transfers is foundational to developing a modern payment strategy. While wires are indispensable for high-value international transactions, legally mandated payments, and scenarios that demand rapid, confirmed settlement, businesses must actively address the substantial hidden costs and procedural complexity they entail.
The defining challenge remains the currency exchange markup, which often overshadows flat transfer fees.
Consequently, the strategic move is toward multi-rail payment platforms and Zero FX Fee solutions. These unified systems consolidate operations, provide greater cost transparency, and leverage alternatives like ACH and in-network transfers, ensuring wires are reserved only for situations where their speed and security uniquely justify the effort.

Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly are B2B wire transfers, and how do they work?
B2B wire transfers represent electronic fund movements between business bank accounts using secure banking networks. The sending bank communicates with recipient banks through systems like SWIFT for international transfers, or Fedwire for domestic US transfers, to transfer funds with immediate availability upon completion.
Processing involves account verification, network routing through correspondent banks for international transfers, and final settlement with confirmation to both parties.
What are Zero FX Fees?
Zero FX Fees (Zero Foreign Exchange Fees) or zero markup are cost-saving features offered by modern financial platforms. They eliminate the currency conversion markup, which is the 1% to 7% surcharge traditional banks typically add on top of the true mid-market exchange rate. By offering the mid-market rate directly, Zero FX Fee platforms, like Bancoli, provide unparalleled transparency and significantly reduce the total cost of international payouts for businesses.
How much do B2B wire transfers cost businesses in 2025?
Wire transfer costs average US$26 for domestic transfers and US$44 for international transfers, according to current banking data. However, total costs, including currency markups (1-7%) and intermediary fees (US$10-US$100), can reach 3-5% of the transfer amounts.
Large transactions exceeding $100,000 result in negligible fees, while smaller payments incur disproportionate cost burdens, affecting profitability.
How long do business wire transfers take to process?
Domestic wire transfers complete within 24 hours during business days. International transfers require 1-5 business days, depending on the countries involved, correspondent banking requirements, and compliance verification needs.
Processing extends during weekends, holidays, and when transactions require manual documentation review or error correction.
What information do businesses need for wire transfers?
Domestic transfers require the recipient’s legal name, bank routing number, account number, and transfer amount. International transfers also require SWIFT codes, IBANs (where applicable), correspondent bank information, and documentation of the payment purpose.
Errors in required information cause processing delays or transaction rejections, particularly for international transfers with complex routing.
Are wire transfers secure for business use?
Wire transfers utilize bank-grade encryption through established financial networks, incorporating multi-factor authentication and verification protocols. However, transactions are irreversible once processed, requiring careful verification before initiation.
Businesses should independently verify recipient information and implement dual authorization procedures for high-value transfers.
When should businesses use wire transfers vs. alternatives?
Use wire transfers for high-value transactions (US$100,000+), emergency payments requiring same-day processing, real estate settlements, or when legal requirements mandate wire confirmation.
Consider alternatives such as ACH networks, digital platforms, or local payment rails for routine operational payments where cost efficiency outweighs the benefits of immediate settlement.
What causes delays in business wire transfer processing?
Common delays include incorrect recipient information, missing documentation, bank cut-off times, processing gaps on weekends, compliance verification holds, and intermediary bank routing requirements.
Manual processes and multiple institution involvement create bottlenecks affecting timing, especially for international transfers requiring correspondent banking.
How do currency conversion costs affect wire transfers?
Traditional banks apply markups of 1-7% above market exchange rates, often resulting in larger costs than base wire fees. Currency conversion timing during multi-day processing creates additional cost uncertainty when rates fluctuate.
A 3% markup on US$100,000 international transfer adds US$3,000 beyond wire fees, substantially impacting total transaction costs.
Can businesses negotiate wire transfer fees?
Large-volume businesses often negotiate enterprise pricing, fee waivers, or volume discounts with traditional banks. Credit unions typically offer fees that are 20-30% lower than those of traditional banks for comparable services.
Mid-market companies rarely qualify for significant discounts, making alternative payment solutions more attractive for cost optimization.
What compliance requirements apply to business wire transfers?
Transfers over US$10,000 trigger federal reporting and enhanced due diligence requirements. International transfers require purpose documentation, beneficiary verification, and compliance with sanctions screening.
Anti-money laundering regulations apply to all wire transfers, with additional requirements for certain countries or industries that banks monitor systematically.
How can businesses effectively reduce wire transfer costs?
Cost reduction strategies include credit union partnerships (averaging 24% savings), volume negotiations with banks, online initiation versus phone/branch processing, and timing optimization to avoid premium charges.
Consider alternative payment methods for routine transactions, reserving wire transfers for scenarios that require their unique, immediate settlement capabilities.
What are the main risks of using wire transfers?
Primary risks include high cumulative costs associated with frequent use, processing delays that affect operations, human error in documentation, exposure to fraud, and the irreversibility of transactions once processed.
Manual processes increase error rates, while limited visibility during processing creates challenges for cash flow forecasting in business operations.




