IBAN numbers serve as the global standard for identifying bank accounts across international borders. For businesses managing cross-border payments, understanding IBAN numbers is essential for efficient international transactions.
The IBAN system streamlines international payments by ensuring accuracy, reducing errors, and accelerating processing times across multiple currencies and countries.
What is an IBAN number?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number. It’s a standardized alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies bank accounts within the banking systems of participating countries.
The IBAN system was introduced in 1997 by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) to simplify cross-border transactions within the European Union (EU).

IBAN Number Format and Structure
IBAN numbers consist of up to 34 alphanumeric characters containing specific information about the bank, country, and individual account. This standardization enables banks worldwide to process cross-border payments accurately, eliminating the need for additional verification steps or correspondent banking relationships.
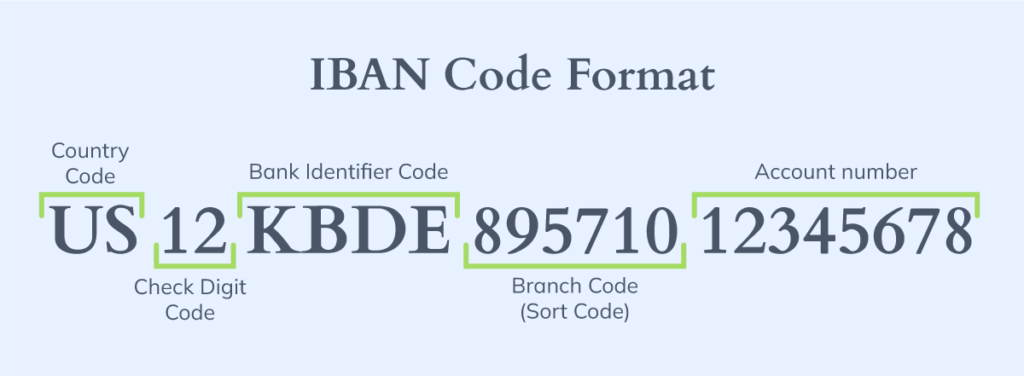
Every international bank account (IBAN) number consists of four essential elements:
- Country Code: Two-letter ISO country identification
- Check Digits: Two-digit validation code for error detection
- Bank Identifier: Institution-specific code (varies by country)
- Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN): Individual account identifier
Standard IBAN Format Structure
IBAN number formats follow ISO 13616 international standards across 80+ participating countries. The standardized structure enables global banks to validate account details automatically and route payments through appropriate banking networks.
For US businesses receiving international payments, understanding IBAN structure explains why American banks require different information (ABA routing numbers + SWIFT codes) compared to European counterparts who use single IBAN identifiers.
IBAN Component Breakdown
- CC (Country Code): Two-letter ISO identification linking accounts to specific national banking regulations and currency systems. This enables automatic compliance screening and regulatory reporting.
- DD (Check Digits): Mathematical validation using mod-97 algorithms that verify IBAN accuracy before processing. Invalid check digits trigger automatic rejection, preventing misdirected payments.
- BBBB (Bank Identifier): Institution-specific codes varying by country’s domestic banking structure. Some countries use bank license numbers, others use standardized institution codes.
- SSSS SS (Branch/Sort Code): Specific branch identification within larger banking organizations, though many modern banks operate without traditional branch-specific routing.
- AA AAAA AAAA (Account Number): Individual account identifier unique within the bank’s customer base, maintaining domestic account numbering while enabling international compatibility.
| Country | IBAN Length | Example Format |
|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 22 characters | GB29 NWBK 6016 1331 9268 19 |
| Germany | 22 characters | DE89 3704 0044 0532 0130 00 |
| France | 27 characters | FR14 2004 1010 0505 0001 3M02 606 |
| Spain | 24 characters | ES91 2100 0418 4502 0005 1332 |
| Italy | 27 characters | IT60 X054 2811 1010 0000 0123 456 |
IBAN vs SWIFT Codes: Understanding the Difference
While both facilitate international banking, IBAN numbers and SWIFT codes serve distinct purposes in cross-border payment processing. Understanding these differences helps businesses manage international bank account operations more effectively.
IBAN numbers identify specific bank accounts within participating countries, while SWIFT codes identify the banks and financial institutions themselves. International wire transfers typically require both identifiers to route payments accurately through global banking networks.
The confusion between these systems often arises because some countries use both, while others, like the United States, rely primarily on SWIFT codes combined with domestic routing systems.
| Feature | IBAN Numbers | SWIFT Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify specific bank accounts | Identify banks and financial institutions |
| Usage | Direct account identification | Route transfers between banks |
| Format | Up to 34 alphanumeric characters | 8-11 alphanumeric characters |
| Scope | Account-level identification | Institution-level identification |
| Example | GB29 NWBK 6016 1331 9268 19 | NWBKGB2L |
IBAN vs. SWIFT/BIC
The term ‘Bank Identification Code’ (BIC) is a SWIFT code alternative. For this reason, BIC and SWIFT codes are often used in combination, referred to as a SWIFT/BIC.
The SWIFT network serves as the platform for international transfers, where BICs (Bank Identifier Codes) are the designated codes employed within this network.
The main difference between IBAN and SWIFT/BIC is that IBAN primarily signifies the bank’s country of operation and the specific account number associated with the individual within that institution. The BIC (Bank Identification Code) provides more specific information to facilitate the transaction.
The SWIFT/BIC code consists of alphanumeric characters, including a 4-letter bank code, a 2-letter country code, and a branch identifier of a letter and a number.
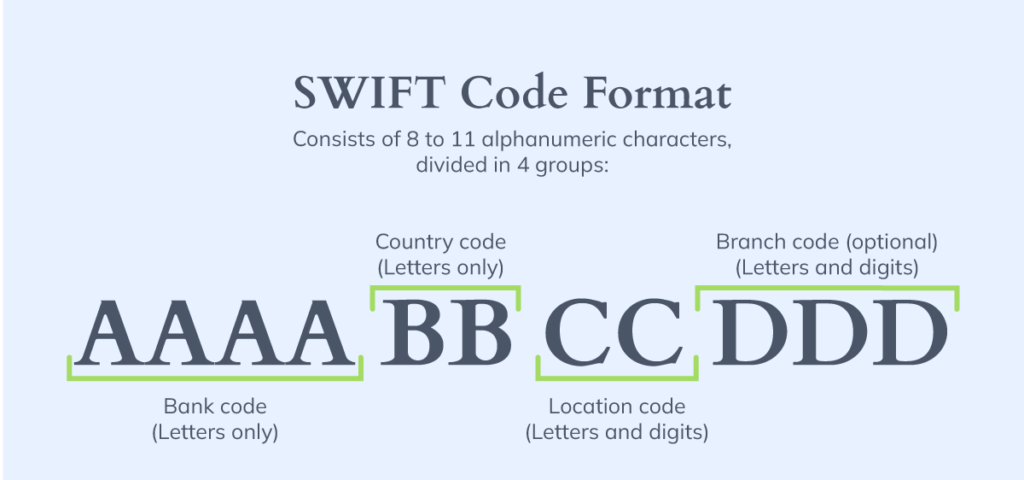
IBAN and SWIFT Working Together
International transfers typically require both identifiers for successful processing. The SWIFT code directs the payment to the correct bank, while the IBAN number identifies the specific recipient account within that institution.
Business payment systems that support multiple international standards eliminate the complexity of managing different identifier requirements across regions.
Companies processing high volumes of international payments benefit from unified platforms that accept various payment rails, including traditional IBAN transfers, US routing numbers, and emerging digital payment methods like stablecoins.
Do US Banks Use IBAN Numbers?
The United States does not use IBAN numbers. This creates confusion for businesses managing cross-border payments between IBAN and non-IBAN countries.
US banks rely on a different system that predates IBAN standardization. When IBAN standards emerged in 1997, America already operated a comprehensive payment infrastructure through the Federal Reserve System, ABA routing networks, and SWIFT membership since 1973.
Converting 5,000+ US banks to IBAN would require massive infrastructure changes without significant benefits. The current system effectively processes international wire transfers through established SWIFT networks.
What Does the USA Use Instead of IBAN?
US banks combine ABA routing numbers (9 digits) with account numbers for domestic transfers, and SWIFT codes for international wire transfers. This multi-identifier approach achieves the same level of account identification as single IBAN numbers in participating countries.
Modern business payment platforms bridge this gap by supporting both IBAN and non-IBAN banking systems, enabling seamless international transactions regardless of regional banking standards.
US Bank International Transfer Requirements
When US businesses receive international payments from IBAN countries, they provide comprehensive banking details that enable correspondent banks to route transfers through the US Federal Reserve networks.
Required Information:
- SWIFT/BIC Code: Bank identification for international transfers
- ABA Routing Number: US domestic bank identifier
- Account Number: Individual account number
- Beneficiary Details: Complete business information
| Feature | US Banking System | IBAN System |
|---|---|---|
| Account Identification | ABA Routing + Account Number | Single IBAN number |
| International Transfers | SWIFT Code + Account Details | IBAN + SWIFT Code |
| Format Length | 9 digits (routing) + variable account | 15-34 characters total |
| Error Detection | Basic validation | Built-in check digits |
| Countries Using | United States only | 80+ countries worldwide |
Countries Using IBAN Numbers
Over 80 countries and territories currently participate in the international bank account numbering system, creating a standardized framework for cross-border payments across multiple regions.
The adoption of the IBAN system varies significantly by geographic region, with European countries showing near-universal implementation, while other regions adopt the standard selectively, based on their existing banking infrastructure and international trade relationships.
Companies trading primarily with European partners benefit from IBAN-compatible payment systems, while those focused on North American or Asian markets may prioritize different payment rails.

European Countries
All European Union member states implement IBAN standards as part of the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) framework. This integration enables same-day EUR transfers between member countries and standardizes payment processing across the eurozone.
Additional European countries have adopted IBAN numbers to facilitate trade with EU partners:
United Kingdom, Norway, Switzerland, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Monaco, San Marino, Andorra, and Vatican City all maintain IBAN compatibility despite varying EU membership status.
Brexit did not affect the UK’s participation in the IBAN system. British businesses continue to use IBAN numbers for international transactions, although the benefits of SEPA instant payments no longer apply.
Middle East and Africa
Middle Eastern countries adopted IBAN standards to support international trade financing and oil commerce settlements. The UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, Jordan, and Lebanon utilize IBAN numbers for both domestic and international banking operations.
African participation remains limited, with Tunisia, Mauritania, Egypt, and Algeria implementing IBAN systems primarily for European trade relationships and remittance processing.
Other Regions
The Americas show selective IBAN adoption, with Brazil, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Virgin Islands participating. These countries typically adopted IBAN standards to facilitate European trade relationships or meet specific regional banking requirements.
Asia Pacific participation includes Pakistan, Kazakhstan, and Georgia, reflecting varied approaches to international banking standardization across the region.
Business payment platforms accommodate this global patchwork by supporting both IBAN and non-IBAN banking systems through multi-currency business accounts and comprehensive payment rail integration.
How to Find and Validate IBAN Numbers
Bank account number identification varies significantly across international banking systems. For businesses managing cross-border transactions, locating and validating IBAN numbers helps prevent payment delays and reduce transfer costs.

Finding Your IBAN Number
If your bank participates in the international bank account system, IBAN numbers appear in multiple locations throughout your banking relationship. The placement and visibility depend on your bank’s digital infrastructure and regional banking practices.
Most European banks prominently display IBAN numbers on account statements and digital platforms. However, businesses should verify the accuracy of IBANs before sharing them with international partners, as errors in international bank account numbers can delay payments by several business days.
- Bank Statements: Usually displayed prominently in account summary sections
- Online Banking: Account details section within digital banking platforms
- Mobile Banking Apps: Account information tabs in modern banking applications
- Bank Customer Service: Direct inquiry through phone or chat support
- Bank Branch: In-person assistance at traditional banking locations
| Method | Location | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Statements | Account summary section | All IBAN banks |
| Online Banking | Account details page | Most digital banks |
| Mobile Banking Apps | Account information tab | Modern banking apps |
| Bank Customer Service | Phone or chat support | All banks |
| Bank Branch | In-person inquiry | Traditional banks |
International Wire Transfer Requirements
Cross-border payment requirements vary significantly between IBAN and non-IBAN banking systems. Understanding these differences helps businesses prepare accurate payment instructions and avoid processing delays.
IBAN Transfer Requirements
When sending payments to IBAN countries, businesses provide standardized information sets that enable direct account identification:
- Recipient IBAN number: Complete international bank account identifier
- Recipient SWIFT/BIC code: Bank and branch identification
- Recipient name and address: Complete beneficiary information
- Transfer purpose/reference: Transaction description for compliance reporting
From Non-IBAN Countries (like the USA)
US businesses sending to IBAN countries need additional documentation due to different banking system requirements:
- Sender’s bank SWIFT code: International identification for originating institution
- Recipient’s complete IBAN: Destination international bank account number
- Correspondent bank details: Intermediate banking relationships if required
- Transfer purpose documentation: Enhanced compliance reporting for cross-border transfers
Modern business payment infrastructure simplifies these requirements by maintaining pre-validated banking relationships and automating documentation requirements across multiple international standards.
IBAN Transfer Processing Times
International IBAN transfers are processed within predictable timeframes, depending on the geographic region, banking relationship, and currency conversion requirements. Understanding these timelines helps businesses plan cash flow and manage payment scheduling effectively.
Processing speeds vary significantly between same-region transfers and cross-border transactions involving correspondent banking networks.
Within SEPA Zone
European Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) transfers benefit from a standardized processing infrastructure:
- Same-day processing: EUR transfers submitted before daily cut-off times
- Next business day: Standard SEPA credit transfers between participating banks
- Instant transfers: Real-time settlement available between participating institutions
SEPA infrastructure enables near-domestic processing speeds for international EUR transfers within participating European countries.

Cross-Border IBAN Transfers
Transfers between different regions require additional processing time due to correspondent banking relationships and enhanced compliance screening:
- Europe to Europe: 1-2 business days for standard processing
- Europe to Middle East: 2-3 business days for cross-region transfers
- To/from non-IBAN countries: 3-5 business days requiring additional routing
Factors Affecting Transfer Speed
Several operational factors influence international bank account transfer processing times:
- Cut-off times: Late submissions automatically process the next business day
- Compliance checks: Enhanced due diligence requirements for certain jurisdictions
- Correspondent banking: Additional routing through intermediate banks increases processing time
- Currency conversion: Foreign exchange processing may add settlement delays
Advanced business payment platforms optimize these timeframes by maintaining direct relationships with multiple banking networks and offering real-time payment processing across various international rails.
| Transfer Type | Processing Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Within SEPA Zone (EUR) | Same day – 1 business day | Before cut-off times |
| Europe to Europe | 1-2 business days | Standard processing |
| Europe to Middle East | 2-3 business days | Cross-region transfers |
| To/from non-IBAN countries | 3-5 business days | Additional routing required |
| Instant SEPA transfers | Under 10 seconds | Participating banks only |
Business payment systems supporting multiple currencies and international bank account standards help companies minimize processing delays while maintaining compliance with global banking regulations.
Business Payment Solutions for International Transactions
Understanding IBAN numbers reveals a fundamental challenge: businesses require unified payment infrastructure that can handle both IBAN and non-IBAN transactions without forcing finance teams to navigate complex technical requirements across different banking systems.
Unified Payment Processing
Modern international businesses require multi-rail payment acceptance that accommodates diverse banking standards and regulations.
Rather than maintaining separate systems for IBAN transfers, US routing numbers, and card processing, unified platforms automatically handle multiple payment rails.
- Accept IBAN transfers from 80+ participating countries
- Process US ACH and wire transfers through domestic networks
- Handle international business card payments across major brands
- Support stablecoin and digital payment methods for 24/7 settlement
Additionally, businesses operating internationally benefit from USD and EUR business accounts that reduce conversion costs and provide local banking details in major markets.
USD accounts integrate with US banking standards while accepting international transfers. EUR accounts provide native IBAN numbers for seamless European transactions.
Bancoli’s Global Payment Gateway and Global Business Account enable businesses to operate like global enterprises without managing multiple vendor relationships or hidden fees across different banking systems.
IBAN Security and Fraud Prevention

International bank account security requires vigilant protection measures, especially as cross-border payment fraud continues evolving. Businesses processing IBAN transfers face specific risks that traditional domestic banking fraud prevention may not adequately address.
IBAN-related fraud typically exploits the complexity of international banking relationships and the difficulty of verifying account details across different jurisdictions and banking systems.
IBAN Verification Best Practices
Protecting your business from international bank account fraud requires systematic verification procedures that go beyond basic IBAN format validation:
- Validate recipient details independently through separate communication channels
- Verify IBAN format and check digits using mathematical validation tools
- Confirm beneficiary identity through separate channels before processing payments
- Document all transfer authorizations with audit trails and approval workflows
- Monitor account activity regularly for unusual patterns or unauthorized access
These verification steps become critical when processing high-value international transfers or establishing new vendor relationships across borders.
Common IBAN Fraud Types
International bank account fraud takes several forms that businesses should recognize:
- IBAN spoofing involves fraudulent substitution of legitimate IBAN numbers in invoices or payment instructions. Criminals intercept business communications and replace valid international bank account numbers with their own accounts.
- Business email compromise targets invoice processing workflows, redirecting payments to fraudulent accounts through sophisticated email manipulation techniques that appear legitimate to finance teams.
- Social engineering attacks convince employees to change payment instructions by claiming false authority or making urgent requests that bypass normal verification procedures.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks intercept payment communications between businesses and their banking partners, substituting fraudulent account details during the transmission process.
Enhanced Security Measures
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) provides multi-layer access control that prevents unauthorized account access even when login credentials are compromised. This becomes especially important for businesses managing multiple international bank account relationships.
- Transaction monitoring systems analyze payment patterns in real-time, flagging suspicious activity before funds are transferred from business accounts. These systems learn normal transaction behaviors and identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Compliance screening automatically checks all international bank account numbers and beneficiary details against global sanctions databases and watchlists, preventing inadvertent violations of international regulations.
- Audit trails maintain complete documentation of all payment authorizations, modifications, and processing steps, supporting both internal compliance requirements and external regulatory reporting obligations.
Implementing international bank account capabilities requires comprehensive planning that addresses payment acceptance, currency management, and operational efficiency considerations.

Future of International Banking Standards
The international bank account numbering system continues expanding beyond its European origins, with new countries evaluating adoption based on trade relationships and regulatory modernization initiatives.
Additional countries join the IBAN system regularly as international trade volumes increase and domestic banking systems modernize. Recent adoptions focus on countries with significant European trade relationships or those seeking to improve international payment efficiency.
Enhanced validation improvements include stronger fraud prevention measures and real-time verification capabilities that reduce payment errors and processing delays across international bank account networks.
Digital integration enables IBAN compatibility with blockchain networks and distributed ledger technologies, bridging traditional banking infrastructure with emerging payment innovations.
Real-time processing capabilities extend beyond SEPA instant payments to encompass global real-time settlement networks, enabling instant cross-border payment capabilities.
Conclusion
IBAN numbers remain fundamental for international business banking, providing standardized account identification across 80+ countries. Understanding IBAN structure, validation, and implementation enables businesses to optimize their global payment operations.
Success in international commerce requires a truly global payment infrastructure that supports multiple standards: IBAN for participating countries, traditional banking systems for non-IBAN regions, and emerging digital payment rails for comprehensive coverage.
Modern business payment platforms streamline the complexity of managing various international banking standards, providing the security, speed, and cost-effectiveness essential for global operations.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is my IBAN number in the USA?
US banks do not issue IBAN numbers. The United States uses ABA routing numbers and account numbers instead. For international transfers, U.S. banks use SWIFT codes to receive payments from countries with IBANs.
How do I find out my IBAN number?
If your bank participates in the IBAN system, find your IBAN on bank statements, online banking platforms, or by contacting your bank directly. Banks in 80+ countries provide IBAN numbers for international account identification.
Is an IBAN the same as a routing number?
No, IBAN numbers and routing numbers serve different purposes. IBANs identify specific bank accounts internationally, while routing numbers identify banks domestically within countries, such as the USA.
Can I use an IBAN instead of a routing number?
IBAN numbers and routing numbers cannot be used interchangeably. Use IBANs for transfers to/from participating countries and routing numbers for domestic US transfers or as required by receiving banks.
What does the USA use instead of an IBAN?
The USA uses ABA routing numbers (9 digits) plus account numbers for domestic transfers, and SWIFT codes for international wire transfers. This system predates the implementation of IBAN and remains the standard for US banking.
Is an IBAN enough for a wire transfer?
IBAN numbers alone may not be sufficient. International transfers often require both the recipient’s IBAN number and the bank’s SWIFT/BIC code to ensure proper routing through correspondent banking networks.
Which bank has an IBAN number?
Banks in IBAN-participating countries issue IBAN numbers. This includes all EU countries plus the UK, Switzerland, Norway, and 70+ other nations. US, Canadian, Australian, and many Asian banks do not use IBANs.
How long does an IBAN transfer take?
IBAN transfer times vary by region: same-day within SEPA zones, 1-2 days within Europe, 2-3 days to Middle East, and 3-5 days for transfers involving non-IBAN countries or complex routing requirements.




